Understanding Device Details & Status
The Device Detail Page is your comprehensive monitoring dashboard for individual devices. It provides asystem complete,information, in-depthresource viewutilization, ofnetwork yourconnectivity device's operational status, technical specifications,details, and networkGPS health.location.
Accessing Device Detail Page
From Device List:
Page Layout Overview
The Device Detail Page uses a two-column layout:
Left Panel: Static device identity and metadata
Right Panel: Dynamic monitoring data across four tabs
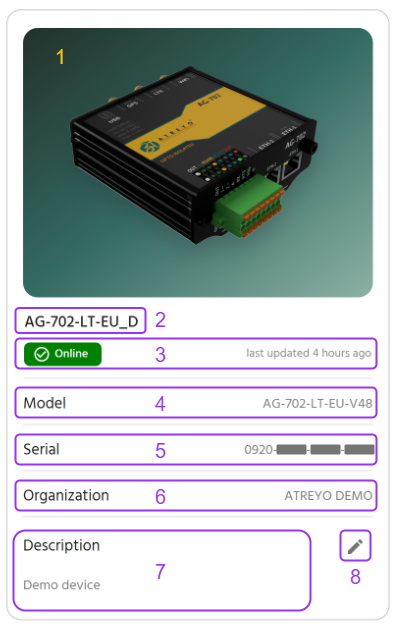
At-a-Glance Information (Left Side)Panel)
The left panel ondisplays the left provides the foundationalcore identity ofand information for your device:device.
# |
Field |
Description |
Example |
|
1 |
Model Image |
Visual representation of |
Gateway illustration |
|
2 |
Device Name |
Custom name |
Delhi_Bus_207 |
|
3 |
Online Status |
Connection |
"Online since |
|
4 |
Model Name |
The specific product name of your |
AG-207-LT-EU |
|
5 |
Serial-ID |
Unique 16-character device identifier |
1A2B-3C4D-5E6F-7G8H |
|
6 |
Organization |
Assigned |
ATREYO |
|
7 |
Description |
Optional |
"Factory Floor A, Bay 3" |
|
8 |
Edit |
Pencil icon to modify description
Detailed View & Monitoring (Right Side)
On the right side, you'll find a Refresh Button and four dedicated tabs for technical monitoring:
Tab 1: Device Information
This tab provides the static, core technical specifications of your device's operating system and internal components.
System✏️ Information
Here are the definitions and examples for the requested System Information parameters:
Modem
Editing Device Description
To Edit Description:
Use Cases for Description Field:
-
Physical location updates
-
Maintenance schedules
-
Contact information for site
-
Network configuration notes
Detailed Monitoring Tabs (Right Panel)
The right panel contains four tabs for in-depth device monitoring. A Refresh button (🔄) in the top-right corner manually updates tab data.
-
Device Information
-
Resource Utilization
-
Network Information
-
GPS Location
Tab 1: Device Information
This tab displays static technical specifications of your device's operating system, hardware, and cellular modem.
Section A: System Information
Core operating system and processor details.
|
Parameter |
Definition |
Example |
OS Name |
Operating |
OpenWRT, |
OS Platform |
OS |
Linux |
OS Version |
Specific |
10.0.22621, |
Architecture |
CPU |
ARMv7l, |
|
Host Name |
Device model name |
AG-702 |
|
Processor Name |
CPU model designation |
MIPS 24KEc V5.5, ARMv7 Processor rev 5 |
Section B: Modem Information
Cellular modem hardware and firmware specifications.
|
Parameter |
Definition |
Example |
|
Model |
Manufacturer's modem product designation |
- |
|
Firmware Version |
Embedded software version number |
V1.01.03, 2.1.25 |
|
IMEI |
International Mobile Equipment Identity (15 digits) |
123456789111111 |
|
Manufacturer |
Company that produced the modem |
- |
Tab 2: Resource Utilization
This sectiontab is your device'sdevice Healthhealth Dashboard,dashboard, showing real-timeperformance performancemetrics and 24-hour historical usage.trends.
Metrics Cards
Three cards display current resource usage across critical components.
CPU Utilization
Displays:
-
Real-Time Data:View the count and utilization percentageNumber of CPU cores, totalRAM size and current usage, andtotal/used storage space. -
PerformanceCurrentGraphs:utilizationSee historical usage trends forCPU, RAM, and Storageover the last 24 hours (data is averaged every 1 minute).percentage
Example:
💡CPU:Health1Insight:Monitoring these resources helps ensure your device is running optimally and not experiencing bottlenecks.cores
Utilization: 45%
RAM Utilization
Displays:
-
Total RAM capacity
-
Currently used RAM
-
Utilization percentage
Example:
RAM: 128 MB total
Used: 66 MB (51.5%)
💡 Memory Management: High RAM usage isn't always problematic. Modern systems use available RAM efficiently. Concern arises when usage stays at 90%+ for extended periods.
Storage Utilization
Displays:
-
Total storage capacity
-
Used storage space
-
Utilization percentage
Example:
Storage: 512 MB total
Used: 270 MB (52.73%)
Common Storage Consumers:
-
Logs
-
Application data
24-Hour Performance Graphs
Below the real-time cards, three line graphs display historical resource usage trends.
Graph Specifications:
-
Time Range: Last 24 hours
-
Data Points: Every 1 minute
-
X-Axis: Time (hours)
-
Y-Axis: Utilization percentage (0-100%)
Graph Types:
-
CPU Usage Graph (Green line)
-
RAM Usage Graph (Blue line)
-
Storage Usage Graph (Yellow line)
Analyzing Performance Trends
Normal Patterns:
CPU:
-
Fluctuates based on workload
-
Spikes during data transmission or processing
-
Should return to baseline after tasks complete
RAM:
-
Typically steady with gradual increases
-
May step up when new processes start
-
Rarely decreases significantly without restart
Storage:
-
Gradually increases over time
-
Sudden jumps indicate large file writes
-
Decreases indicate log rotation or cleanup
Tab 3: Network Information
TrackThis thetab connectionprovides statusdetailed andconnectivity data usageinformation for both wired (Ethernet) and cellularwireless (Cellular) network interfaces.
The tab is organized into two sections:
-
Ethernet Card Information
-
Cellular Card Information
Section A: Ethernet Card Information
Wired network interface details for WAN (internet) and LAN (local network) connections.
Typical Display: Multiple ethernet interfaces may be shown (e.g., WAN, LAN, LAN2)
Ethernet Parameters
Parameter |
Definition |
Example |
Interface Name |
Logical network function identifier |
WAN ( |
Interface Device |
OS-assigned hardware identifier |
eth0.1 (VLAN sub-interface), |
|
IPv4 Address |
Network address for IPv4 communication |
192.168.1.1 (router), |
|
MAC Address |
Unique 12-digit hardware identifier |
00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E |
|
Download Speed |
Current incoming data transfer rate |
100 Mbps, 1 Gbps |
|
Upload Speed |
Current outgoing data transfer rate |
50 Mbps, 900 Mbps |
|
Downloaded Data |
Total data received since last reset |
5.2 GB, 1.3 TB |
|
Uploaded Data |
Total data transmitted since last reset |
850 MB, 450 GB |
IMSI,
Section B: Cellular Card Information
Wireless cellular network connectivity details for mobile or backup internet connections.
Cellular Parameters
|
Parameter |
Definition |
Example |
|
Operator |
Telecommunications carrier providing service |
Vodafone, AT&T, T-Mobile, Airtel |
|
APN |
Access Point Name - Gateway for mobile internet |
internet.voda.ie, broadband, airtelgprs.com |
|
IMSI |
International Mobile Subscriber Identity (15 digits) |
310410123456789 |
|
IPv4 |
Mobile network IP address (version 4) |
10.123.45.67 (carrier private IP) |
|
IPv6 |
Mobile network IP address (version 6) |
2001:0db8:85a3::8a2e:0370:7334 |
|
MSISDN |
SIM card number |
+447700900000, 5551234567 |
|
ICCID |
Integrated Circuit Card ID - SIM serial number |
89014103210123456789 |
|
Signal Strength |
Cellular signal quality in dBm |
-75 dBm (excellent), |
|
Downloaded Data |
Total |
2.1 GB |
|
Uploaded Data |
Total cellular data transmitted |
450 MB |
Ethernet
Interpreting Information:Signal Strength
Signal strength is measured in dBm (decibel-milliwatts), a logarithmic scale where higher (less negative) values indicate stronger signals.
HereSignal areQuality the definitions and examples for the Ethernet card parameters:Scale:
dBm Range |
Quality |
Description |
Connectivity |
-50 to -70 |
Excellent |
Strong, clear signal |
Full-speed data, reliable |
-70 to -85 |
Good |
Adequate signal |
Good data speeds, stable |
-85 to -100 |
Fair |
Weak |
Reduced |
-100 to -110 |
Poor |
Very |
Slow speeds, frequent disconnects |
-110 to -120 |
Critical |
Barely | |
Unusable, | |||
Factors Affecting Signal:
-
Distance from cell tower
-
Physical obstructions (buildings, terrain)
-
Weather conditions
-
Network congestion
-
Antenna quality and positioning
Cellular Troubleshooting Quick Guide
Problem: Poor Signal Strength (<-100 dBm)
Solutions:
-
Antenna Positioning: Relocate device or adjust external antenna
-
Alternative Location: Move device to higher elevation or near window
Problem: No Cellular Card Information:Connection
HereCheck:
-
definitions✅ SIM card inserted correctly
-
✅ Carrier account is active and
examplespaid -
✅ APN settings match carrier requirements
-
✅ Device is in carrier coverage area
-
✅ IMEI is not blocked by carrier
Problem: High Data Usage
Investigate:
-
Check Downloaded/Uploaded Data totals
-
Review application data transmission settings
-
Confirm data is being sent via cellular (not ethernet)
-
Look for unauthorized usage or malware
Tab 4: GPS Location
This tab manages device location tracking through automatic GPS data or manual coordinate entry.
Location Tracking Modes
The tab offers two mutually exclusive modes:
-
Auto Mode: Automatic GPS tracking
-
Manual Mode: User-defined coordinates
Option A: Auto Mode
Automatic location tracking using the device's internal GPS modem.
How It Works:
-
Device's cellular
cardmodeminformation:contains GPS receiver -
Modem locks onto GPS satellites (requires 4+ satellites)
-
Location data calculated on device
-
Coordinates transmitted to Atra RMS
-
Map updates automatically
GPS Data Fields
When Auto mode is active and GPS has a fix, the following data is displayed:
Field |
Description |
Example |
Coordinates |
Latitude |
23.0225° |
Altitude |
Height |
45 meters (147.6 feet) |
Speed |
Current |
60 km/h ( |
Direction/Course |
Compass |
270° (West), 45° (Northeast) |
Fix |
Position |
"3D Fix" (lat, lon, alt) |
Satellites |
Number |
8 satellites |
HDOP |
Horizontal |
1.2 ( |
Validity |
Data |
'A' ( |
invalid)
Tab 4: GPS Location
This tab manages how the device's physical location is tracked. You have two options: Auto or Manual.
Option: Auto (Recommended for Mobile Devices)
The device automatically sends location data obtained from its modem to the cloud. This is ideal for devices mounted on vehicles or where real-time location tracking is essential.
GPS Time |
Timestamp |
2025-12-31 | |
Option:Understanding ManualGPS Accuracy
IfSatellites theCount:
-
4+ satellites: Minimum for 3D fix (lat, lon, altitude)
-
3 satellites: 2D fix only (lat, lon, no altitude)
-
8-12 satellites: Optimal accuracy
-
<3 satellites: No position fix possible
HDOP (Horizontal Dilution of Precision):
-
Quality Indicator: Lower values = better accuracy
-
Scale:
-
1.0-2.0: Excellent (typical accuracy: 1-3 meters)
-
2.0-5.0: Good (typical accuracy: 3-10 meters)
-
5.0-10.0: Moderate (typical accuracy: 10-30 meters)
-
>10.0: Poor (accuracy degraded)
Validity Codes:
-
'A' (Active/Valid): GPS data is current and reliable
-
'V' (Void/Invalid): GPS data is stale or unreliable
GPS Troubleshooting
Problem: No GPS Fix
Common Causes:
-
❌ Device is indoors (GPS requires clear sky view)
-
❌ Device is in metal enclosure (blocks signals)
-
❌ GPS antenna not connected properly
-
❌ Location service disabled in device settings
Solutions:
-
Move Device: Place near window or outdoors temporarily
-
Check Antenna: Verify external GPS antenna connection
-
Wait: First fix can take 5-15 minutes ("cold start")
-
Verify Settings: Ensure GPS service is
disabledenabled
Problem: Poor Accuracy (High HDOP)
Solutions:
-
Improve Sky View: Remove obstructions above device
-
Wait: Accuracy improves as more satellites are acquired
-
External Antenna: Use high-quality external GPS antenna
-
Check Environment: Avoid placement near RF interference sources
Use Cases for Auto GPS Mode
Ideal Scenarios:
-
✅ Vehicle-mounted devices (fleet tracking)
-
✅ Mobile equipment monitoring
-
✅ Temporary installations requiring location verification
-
✅ Asset tracking applications
-
✅ Devices requiring location-based automation
Not Recommended:
-
❌ Stationary indoor installations
-
❌ Underground or
unavailable,heavilyyoushieldedcanlocationsmanually -
the❌
device'sLocations with poor GPS visibility
Option B: Manual Mode
User-defined static location (coordinates.
How It Works:
-
User enters Latitude and
Longitude).Longitude manually -
Coordinates stored in cloud only
-
Location displayed on Overview map
-
No data transmitted from device
Manual Location Entry
Input Fields:
Latitude:
-
Format: Decimal degrees
-
Range: -90° to +90°
-
North: Positive values
-
South: Negative values
-
Example: 23.0225 (23° N)
Longitude:
-
Format: Decimal degrees
-
Range: -180° to +180°
-
East: Positive values
-
West: Negative values
-
Example: 72.5714 (72° E)
Finding Coordinates for Manual Entry
Method 1: Google Maps
-
Open Google Maps (maps.google.com)
-
Right-click on desired location
-
Click "What's here?"
-
Coordinates appear at bottom (click to copy)
-
Format: Latitude, Longitude (e.g., 23.0225, 72.5714)
Method 2: GPS Device/Phone
-
Use smartphone GPS app
-
Stand at device location
-
Record coordinates from app
-
Enter into Manual Location fields
Method 3: Physical Address Lookup
-
Use geocoding service (e.g., geocode.xyz)
-
Enter physical address
-
Service returns coordinates
-
Verify accuracy on map before using
Important Limitations of Manual Mode
⚠️ ImportantCritical Note:Understanding:
Manual location data is stored onlyONLY in the cloudcloud, and notNOT on the device. The physical location of the device may differ from the location you set manually.
device.
Implications:
💭FAQs
How do I get to the Device Detail Page?
From the Device List Page, simply click on the name of the device you wish to inspect. This will take you directly to its detail page.
What is the most important information on the Device Detail Page for troubleshooting?
Look at the Resource Utilization tab. This section shows real-time usage for CPU, RAM, and Storage, along with 24-hour historical graphs. This data gives you immediate insight into the device's health and performance.
What does a low HDOP value mean in the GPS Location tab?
HDOP stands for Horizontal Dilution of Precision. A low HDOP value (typically between 1 and 2) is a good thing! It means the satellite signals are well-distributed, giving you a more accurate device position.
What's the difference between "Auto" and "Manual" GPS location?
-
Auto:MapTheDisplay:deviceDeviceautomaticallyappearssendsatreal-timemanual locationdataongatheredOverviewfrom its internal modem.map -
Manual:DeviceYouReality:manuallyPhysicalenterdevicethehascoordinates.noThisknowledgedataofisthisstoredlocationonly -
theMismatch
cloud,Possible:notDeviceonmaythebedevice,physicallyand is used when the device's physical GPS service is unavailable.elsewhere
⚠️ Use Manual Mode Only When:
Use Cases for Manual Mode
Appropriate Scenarios:
-
✅ Fixed indoor installations (factories, server rooms)
-
✅ Underground installations (basements, tunnels)
-
✅ Devices in GPS-shielded enclosures
-
✅ Legacy devices without GPS capability
-
✅ Approximate location sufficient for inventory purposes
Not Recommended:
-
❌ Mobile devices requiring real-time tracking
-
❌ Situations requiring precise location verification
-
❌ Applications with location-based automation
-
❌ Compliance scenarios requiring actual device location